 Biomedicine is doing some amazing things these days, so much so that I can hardly keep up with the rate of developments. Just last month, two amazing ones were made, offering new solutions for replacing human tissue and treating chronic conditions. The first has to do with a new method of growing human using a patients own DNA, while the second involves using a patient’s own heart tissue to create “mini hearts” to aid in circulation.
Biomedicine is doing some amazing things these days, so much so that I can hardly keep up with the rate of developments. Just last month, two amazing ones were made, offering new solutions for replacing human tissue and treating chronic conditions. The first has to do with a new method of growing human using a patients own DNA, while the second involves using a patient’s own heart tissue to create “mini hearts” to aid in circulation.
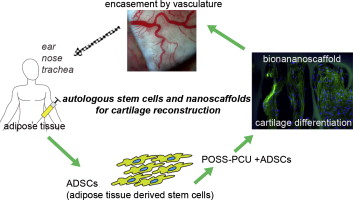
The first comes from London’s Great Ormond Street Hospital, where researchers are working on a process that will grow human ears using genetic material taken from a patient’s own fat tissue. Building upon recent strides made in the field of bioprinting, this process will revolution reconstructive surgery as we know it. It also seeks to bring change to an area of medicine which, despite being essential for accident victims, has been sadly lacking in development.
 Currently, the procedure to repair damaged or non-existent cartilage in the ear involves an operation that is usually carried out when the patient is a child. For the sake of this procedure, cartilage is extracted from the patient’s ribs and painstakingly crafted into the form of an ear before being grafted back onto the individual. Whilst this method of reconstruction achieves good results, it also comes with its share of unpleasant side effects.
Currently, the procedure to repair damaged or non-existent cartilage in the ear involves an operation that is usually carried out when the patient is a child. For the sake of this procedure, cartilage is extracted from the patient’s ribs and painstakingly crafted into the form of an ear before being grafted back onto the individual. Whilst this method of reconstruction achieves good results, it also comes with its share of unpleasant side effects.
Basically, the patient is left with a permanent defect around the area from where the cells were harvested, as the cartilage between the ribs does not regenerate. In this new technique, the cartilage cells are engineered from mesenchymal stem cells, extracted from the child’s abdominal adipose (fat) tissue. The benefit of this new system is that unlike the cartilage in the ribs, the adipose tissue regenerates, therefore leaving no long-term defect to the host.
 There is also the potential to begin reconstructive treatment with stem cells derived from adipose tissue earlier than previously possible, as it takes time for the ribs to grow enough cartilage to undergo the procedure. As Dr. Patrizia Ferretti, a researcher working on the project, said in a recent interview:
There is also the potential to begin reconstructive treatment with stem cells derived from adipose tissue earlier than previously possible, as it takes time for the ribs to grow enough cartilage to undergo the procedure. As Dr. Patrizia Ferretti, a researcher working on the project, said in a recent interview:
One of the main benefits in using the patient’s own stem cells is that there is no need for immune suppression which would not be desirable for a sick child, and would reduce the number of severe procedures a child needs to undergo.
To create the form of the ear, a porous polymer nano-scaffold is placed in with the stem cells. The cells are then chemically induced to become chondrocytes (aka. cartilage cells) while growing into the holes in the scaffold to create the shape of the ear. According to Dr. Ferretti, cellularized scaffolds – themselves a recent medical breakthrough – are much better at integrating than fully-synthetic implants, which are more prone to extrusion and infection.
While we are developing this approach with children with ear defects in mind, it could ultimately be utilized in other types of reconstructive surgery both in children and adults.
Basically, this new, and potentially more advantageous technique would replace the current set of procedures in the treatment of defects in cartilage in children such as microtia, a condition which prevents the ear from forming correctly. At the same time, the reconstructive technology also has the potential to be invaluable in improving the quality of life of those who have been involved in a disfiguring accident or even those injured in the line of service.
 Next up, there is the “mini heart” created by Dr. Narine Sarvazyan of George Washington University in Washington D.C.. Designed to be wrapped around individual veins, these cuffs of rhythmically-contracting heart tissue are a proposed solution to the problem of chronic venous insufficiency – a condition where leg veins suffer from faulty valves, which prevents oxygen-poor blood from being pumped back to the heart.
Next up, there is the “mini heart” created by Dr. Narine Sarvazyan of George Washington University in Washington D.C.. Designed to be wrapped around individual veins, these cuffs of rhythmically-contracting heart tissue are a proposed solution to the problem of chronic venous insufficiency – a condition where leg veins suffer from faulty valves, which prevents oxygen-poor blood from being pumped back to the heart.
Much like process for creating replacement ears, the mini hearts are grown by coaxing a patient’s own adult stem cells into becoming cardiac cells. When one of those cuffs is placed around a vein, its contractions aid in the unidirectional flow of blood, plus it helps keep the vein from becoming distended. Additionally, because it’s grown from the patient’s own cells, there’s little chance of rejection. So far, the cuffs have been grown in the lab, where they’ve also been tested. But soon, Sarvazyan hopes to conduct animal trials.
 As Sarvazyan explained, the applications here far beyond treating venous insufficiency. In addition, there are the long-range possibilities for organ replacement:
As Sarvazyan explained, the applications here far beyond treating venous insufficiency. In addition, there are the long-range possibilities for organ replacement:
We are suggesting, for the first time, to use stem cells to create, rather than just repair damaged organs. We can make a new heart outside of one’s own heart, and by placing it in the lower extremities, significantly improve venous blood flow.
One of the greatest advantages of the coming age of biomedicine is the ability to replace human limbs, organs and tissue using organic substitutions. And the ability to grow these from the patient’s own tissue is a major plus, in that it cuts down on the development process and ensures a minimal risk of rejection. On top of all that, the ability to create replacement organs would also significantly cut down on the costs of replacement tissue, as well as the long waiting periods associated with donor lists.
Imagine that, if you will. A future where a patient suffering from liver, kidney, circulatory, or heart problems is able to simply visit their local hospital or clinic, donate a meager supply of tissue, and receive a healthy, fully-compatible replacement after an intervening period (days or maybe even hours). The words “healthy living” will achieve new meaning!
Sources: gizmag.com, (2), nanomedjournal.com














