 When it comes to classic and hard science fiction, there are few concepts more inspired, more audacious, and more cool than the Space Elevator. Consisting of a cable (or tether) attached the Earth near the equator and a station in geosynchronous orbit, a structure of this kind would allow us to put objects, supplies and even people into orbit without the need for rockets and space ships.
When it comes to classic and hard science fiction, there are few concepts more inspired, more audacious, and more cool than the Space Elevator. Consisting of a cable (or tether) attached the Earth near the equator and a station in geosynchronous orbit, a structure of this kind would allow us to put objects, supplies and even people into orbit without the need for rockets and space ships.
And perhaps I am a bit biased, seeing as how one of the writer’s featured in the Yuva anthology happens to have written a story that features one – Goran Zidar, whose story “Terraformers” includes an orbital colony that is tethered to the planet by a “Needle”. But I’ve found the concept fascinating for as long as I have known about it, and feel like its time for a conceptual post that deals with this most awesome of concepts!
Here goes…
History:
The first recorded example of the space elevator concept appeared in 1895 when Russian scientist Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was inspired by the Eiffel Tower in Paris. He considered a similar tower that extended from the ground into geostationary orbit (GSO) in space. Objects traveling into orbit would attain orbital velocity as they rode up the tower, and an object released at the tower’s top would also have the velocity necessary to remain in orbit.
 However, his concept called for a compression structure, which was unfeasible given that no material existed that had enough compressive strength to support its own weight under such conditions. In 1959, another Russian scientist named Yuri N. Artsutanov suggested a more feasible proposal, a tensile structure which used a geostationary satellite as the base from which to deploy the structure downward.
However, his concept called for a compression structure, which was unfeasible given that no material existed that had enough compressive strength to support its own weight under such conditions. In 1959, another Russian scientist named Yuri N. Artsutanov suggested a more feasible proposal, a tensile structure which used a geostationary satellite as the base from which to deploy the structure downward.
By using a counterweight, a cable would be lowered from geostationary orbit to the surface of Earth, while the counterweight was extended from the satellite away from Earth, keeping the cable constantly over the same spot on the surface of the Earth. He also proposed tapering the cable thickness so that the stress in the cable was constant. This gives a thinner cable at ground level that becomes thicker up towards the GSO.
 In 1966, Isaacs, Vine, Bradner and Bachus, four American engineers, reinvented the concept under the name “Sky-Hook”. In 1975, the concept was reinvented again by Jerome Pearson, whose model extended the distance of the counterweight to 144,000 km (90,000 miles) out, roughly half the distance to the Moon. However, these studies were also marred by the fact that no known material possessed the tensile strength required.
In 1966, Isaacs, Vine, Bradner and Bachus, four American engineers, reinvented the concept under the name “Sky-Hook”. In 1975, the concept was reinvented again by Jerome Pearson, whose model extended the distance of the counterweight to 144,000 km (90,000 miles) out, roughly half the distance to the Moon. However, these studies were also marred by the fact that no known material possessed the tensile strength required.
By the turn of the century, however, the concept was revitalized thanks to the development of carbon nanotubes. Believing that the high strength of these materials might make an orbital skyhook feasible, engineer David Smitherman of NASA put together a workshop at the Marshall Space Flight Center and invited many scientists and engineers to participate. Their findings were published in an article titled “Space Elevators: An Advanced Earth-Space Infrastructure for the New Millennium”.
 Another American scientist, Bradley C. Edwards, also suggested using nanotubes to create a 100,000 km (62,000 mile) paper-thin cable that would be shaped like a ribbon instead of circular. This, he claimed, would make the tether more resistant to impacts from meteoroids. The NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts began supporting Edwards’ work, allowing him to expand on it and plan how it would work in detail.
Another American scientist, Bradley C. Edwards, also suggested using nanotubes to create a 100,000 km (62,000 mile) paper-thin cable that would be shaped like a ribbon instead of circular. This, he claimed, would make the tether more resistant to impacts from meteoroids. The NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts began supporting Edwards’ work, allowing him to expand on it and plan how it would work in detail.
In Fiction:
 In 1979, the concept of the Space Elevator was introduced to the reading public thanks to the simultaneous publications of Arthur C. Clarke’s The Fountains of Paradise (1979) and Charles Sheffield’s The Web Between the Worlds. In the former, engineers construct a space elevator on top of a mountain peak in the fictional island country of Taprobane, which was loosely based on Clarke’s new home in Sri Lanka, albeit moved south to the Equator.
In 1979, the concept of the Space Elevator was introduced to the reading public thanks to the simultaneous publications of Arthur C. Clarke’s The Fountains of Paradise (1979) and Charles Sheffield’s The Web Between the Worlds. In the former, engineers construct a space elevator on top of a mountain peak in the fictional island country of Taprobane, which was loosely based on Clarke’s new home in Sri Lanka, albeit moved south to the Equator.
In an interesting and fact-based twist, the purpose for building the elevator on Earth is to demonstrate that it can be done on Mars. Ultimately, the protagonist of the story (Dr Vannevar Morgan) is motivated by his desire to help a Mars-based consortium to develop the elevator on Mars as part of a massive terraforming project, something which has been proposed in real life.
 Similiarly, in Sheffield’s Web, which was his first novel, we see a world famous engineer who has created extensive bridge networks all over the world using graphite cable. In hoping to achieve the unachievable dream, he begins work on a space elevator code named the “Beanstalk”. This brings him into an alliance with a corrupt tycoon who wants to make rockets obsolete, and intrigue ensues…
Similiarly, in Sheffield’s Web, which was his first novel, we see a world famous engineer who has created extensive bridge networks all over the world using graphite cable. In hoping to achieve the unachievable dream, he begins work on a space elevator code named the “Beanstalk”. This brings him into an alliance with a corrupt tycoon who wants to make rockets obsolete, and intrigue ensues…
Three years later, Robert A. Heinlein’s novel Friday features a space elevator known as the “Nairobi Beanstalk”. In Heinlein’s vision, the world of the future is heavily Balkanized, and people exist in thousands of tiny nation states and orbital colonies which are connected to Earth via the Beanstalk, which as the name suggests, is located in equatorial Africa.
 In 1993, Kim Stanley Robinson released Red Mars, a sci-fi classic that remains a quintessential novel on the subject of Mars colonization. In the novel, the Martian colonists build a space elevator that allows them to bring additional colonists to the surface, as well as transport natural resources that were mined planetside into orbit where they can be ferried back to Earth.
In 1993, Kim Stanley Robinson released Red Mars, a sci-fi classic that remains a quintessential novel on the subject of Mars colonization. In the novel, the Martian colonists build a space elevator that allows them to bring additional colonists to the surface, as well as transport natural resources that were mined planetside into orbit where they can be ferried back to Earth.
In 1999, Sid Meier’s, creator of the famed Civilization gaming series, released the sci-fi based Sid Meier’s Alpha Centauri that deals with the colonization of the planet “Chiron” in the Alpha Centauri system. In the course of the turn-based strategy game, players are encouraged to construct special projects as a way of gaining bonuses and building up their faction’s power.
One such project is the Space Elevator, which requires that the faction building first research the technology “super tensile solids” so they have the means of building a super-tensile tether. Once built, it confers bonuses for space-based unit production, allows orbital drop units to be deployed over the entire planet, increases production rates for satellites, and removes the need for aerospace facilities.  In David Gerrold’s 2000 novel, Jumping Off The Planet, we are again confronted with an equatorial space elevator, this time in Ecuador where the device is once again known as the “beanstalk”. The story focuses on a family excursion which is eventually revealed to be a child-custody kidnapping. In addition to this futuristic take on domestic issues, Gerrold also examined some of the industrial applications of a mature elevator technology.
In David Gerrold’s 2000 novel, Jumping Off The Planet, we are again confronted with an equatorial space elevator, this time in Ecuador where the device is once again known as the “beanstalk”. The story focuses on a family excursion which is eventually revealed to be a child-custody kidnapping. In addition to this futuristic take on domestic issues, Gerrold also examined some of the industrial applications of a mature elevator technology.
 In 2001, Alastair Reynolds, a hard sci-fi author and creator of the Revelation Space series, released Chasm City, which acted as a sort of interquel between the first and second books in the main trilogy. At the opening of the novel, the story takes place on Sky’s Edge, a distant world where settlers travel to and from ships in orbit using a space elevator that connects to the planetary capitol on the surface.
In 2001, Alastair Reynolds, a hard sci-fi author and creator of the Revelation Space series, released Chasm City, which acted as a sort of interquel between the first and second books in the main trilogy. At the opening of the novel, the story takes place on Sky’s Edge, a distant world where settlers travel to and from ships in orbit using a space elevator that connects to the planetary capitol on the surface.
And in 2011, author Joan Slonczewski presented a biological twist on the concept with her novel The Highest Frontier. Here, she depicts a college student who ascends a space elevator that uses a tether constructed from self-healing cables of anthrax bacilli. The engineered bacteria can regrow the cables when severed by space debris, thus turning the whole concept of tensile solids on its head.
Attempts to Build a Space Elevator:
Since the onset of the 21st century, several attempts have been made to design, fund, and create a space elevator before the end of this century. To speed the development process, proponents of the concept have created several competitions to develop the relevant technologies. These include the Elevator: 2010 and Robogames Space Elevator Ribbon Climbing, annual competitions seeking to design climbers, tethers and power-beaming systems.
 In March of 2005, NASA announced its own incentive program, known as the Centennial Challenges program, which has since merged the Spaceward Foundation and upped the total value of their cash prizes to US$400,000. In that same year, the LiftPort Group began producing carbon nanotubes for industrial use, with the goal of using their profits as capital for the construction of a 100,000 km (62,000 mi) space elevator.
In March of 2005, NASA announced its own incentive program, known as the Centennial Challenges program, which has since merged the Spaceward Foundation and upped the total value of their cash prizes to US$400,000. In that same year, the LiftPort Group began producing carbon nanotubes for industrial use, with the goal of using their profits as capital for the construction of a 100,000 km (62,000 mi) space elevator.
In 2008, the Japanese firm known as the Space Elevator Association, chaired by Shuichi Ono, announced plans to build a Space Elevator for the projected price tag of a trillion yen ($8 billion). Though the cost is substantially low, Ono and his peers claimed that Japan’s role as a leader in the field engineering could resolve the technical issues at the price they quoted.
 In 2011, Google was reported to be working on plans for a space elevator at its secretive Google X Lab location. Since then, Google has stated that it is not working on a space elevator. But in that same year, the first European Space Elevator Challenge (EuSEC) to establish a climber structure took place in August.
In 2011, Google was reported to be working on plans for a space elevator at its secretive Google X Lab location. Since then, Google has stated that it is not working on a space elevator. But in that same year, the first European Space Elevator Challenge (EuSEC) to establish a climber structure took place in August.
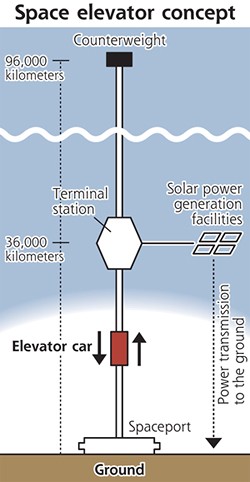
And in 2012, the Obayashi Corporation of Japan announced that in 38 years it could build a space elevator using carbon nanotube technology. Their detailed plan called for a 96,000 long tether, supported by a counterweight, that could hold a 30-passenger climber that would travel 200 km/h, reaching the GSO after a 7.5 day trip. However, no cost estimates, finance plans, or other specifics were made at this point.
 Despite these efforts, the problems of building are still marred by several technical issues that have yet to be resolved. These include the problems of tensile strength, dangerous vibrations along the tether line, climbers creating wobble, dangers posed by satellites and meteoroids, and the fact that such a structure would be vulnerable to a terrorist or military attack.
Despite these efforts, the problems of building are still marred by several technical issues that have yet to be resolved. These include the problems of tensile strength, dangerous vibrations along the tether line, climbers creating wobble, dangers posed by satellites and meteoroids, and the fact that such a structure would be vulnerable to a terrorist or military attack.
Other Possibilities:
Though we may never be able to resolve the problems of building a space elevator on Earth, scientists are agreed that one could be made on other planets, particularly the Moon. This idea was first devised by Jerome Pearson, one of the concepts many original proponents, who proposed a smaller elevator that would be anchored by Earth’s gravity field.
 This is a necessity since the Moon does not rotate and could therefore not maintain tension along a tether. But in this scenario, the cable would be run from the moon and out through the L1 Lagrangian point. Once there, it would be dangled down into Earth’s gravity field where it would be held taught by Earth gravity and a large counterweight attached to its end.
This is a necessity since the Moon does not rotate and could therefore not maintain tension along a tether. But in this scenario, the cable would be run from the moon and out through the L1 Lagrangian point. Once there, it would be dangled down into Earth’s gravity field where it would be held taught by Earth gravity and a large counterweight attached to its end.
Since the Moon is a far different environment than planet Earth, it presents numerous advantages when building a space elevator. For starters, there’s the strength of the materials needed, which would be significantly less, thus resolving a major technical issue. In addition, the Moon’s lower gravity would mean a diminished weight of the materials being shipped and of the structure itself.
 As Pearson explained:
As Pearson explained:
[T]o lift a thousand tons per day off the lunar surface, it would take less than 100,000 tons of elevator to do it — which means it pays back its own mass in just 100 days, or somewhere between three and four times its own mass per year — which is not a bad rate of return… You don’t need nanotubes and very, very high strength materials. But the higher the strength, the more of the ratio you can get for hauling stuff on the moon.
In fact, LiftPort is already deep into developing a “Lunar Elevator”. Plans to build one by 2020 were announced back in 2010, and since that time, the company launched a Kickstarter campaign to get the funding necessary to conduct tests that will get them closer to this goal. These consisting of sending a tethered robot 2km from the surface to conduct stress and telemetry tests.
Ultimately, the company estimates that a Lunar Elevator could be made at the cost of $800 million, which is substantially less than a “Terran Elevator” would cost. Similarly, it is likely that any manned missions to Mars, which will include eventual settlement and plans to terraform, will involve a Martian elevator, possibly named the “Ares Elevator”.
Much like SpaceX’s attempts to resolve the costs of sending rockets into space, the concept of a space elevator is another means of reducing the cost of sending things into orbit. As time goes on and technology improves, and humanity finds itself in other terrestrial environments where resources need to be exported into space, we can expect that elevators that pierce the sky will become possible.
In the meantime, we can always dream…
 Sources: en.wikepedia.org, gizmag.com, io9.com, forbes.com, universetoday.com, futuretimeline.com
Sources: en.wikepedia.org, gizmag.com, io9.com, forbes.com, universetoday.com, futuretimeline.com
 The moon remains the focal point of much of our space-related goals for the near future. In addition to China recently landing its Jade Rabbit probe, the more ambitious plans of NASA and the ESA involve building a settlement there in the near future. But of course, these and other plans to turn the moon into a new frontier from humanity are marred by the fact the environment is not habitable.
The moon remains the focal point of much of our space-related goals for the near future. In addition to China recently landing its Jade Rabbit probe, the more ambitious plans of NASA and the ESA involve building a settlement there in the near future. But of course, these and other plans to turn the moon into a new frontier from humanity are marred by the fact the environment is not habitable. Plants react to aspects of a harsh environment similarly to humans, as their genetic material can be damaged by radiation. A relatively safe way to test long-term lunar exposure is to send plants there and monitor their health. Rather than making the trip and dropping the plants off itself, NASA plans to use commercial spaceflight as the vehicle by which the plants will be sent up to the moon.
Plants react to aspects of a harsh environment similarly to humans, as their genetic material can be damaged by radiation. A relatively safe way to test long-term lunar exposure is to send plants there and monitor their health. Rather than making the trip and dropping the plants off itself, NASA plans to use commercial spaceflight as the vehicle by which the plants will be sent up to the moon. Once the lander arrives on the moon, water will be added to the basil, turnip, and Arabidopsis (a small flowering plant) seeds kept in the habitat, then monitored for five to ten days and compared to control groups germinating back on Earth. NASA will also monitor the actual habitat itself, looking toward its scalability since the small habitat isn’t large enough to support human life.
Once the lander arrives on the moon, water will be added to the basil, turnip, and Arabidopsis (a small flowering plant) seeds kept in the habitat, then monitored for five to ten days and compared to control groups germinating back on Earth. NASA will also monitor the actual habitat itself, looking toward its scalability since the small habitat isn’t large enough to support human life.  If NASA doesn’t run into any unexpected bumps, its long-term plans include attempting to grow a more diverse array of plants, longer growth periods, and reproduction experiments. The longer the experiments, the more we’ll learn about the long-term effects of a lunar environment on Earth plants, which will tell us much of what we need to know if we ever plan on building true settlements there in the future.
If NASA doesn’t run into any unexpected bumps, its long-term plans include attempting to grow a more diverse array of plants, longer growth periods, and reproduction experiments. The longer the experiments, the more we’ll learn about the long-term effects of a lunar environment on Earth plants, which will tell us much of what we need to know if we ever plan on building true settlements there in the future.






















































