I love to study this thing we call “the future”, and began to do so as a hobby the day I made the decision to become a sci-fi writer. And if there’s anything I’ve learned, its that the future is an intangible thing, a slippery beast we try to catch by the tail at any given moment that is constantly receding before us. And when predict it, we are saying more about the time in which we are living than anything that has yet to occur.
I love to study this thing we call “the future”, and began to do so as a hobby the day I made the decision to become a sci-fi writer. And if there’s anything I’ve learned, its that the future is an intangible thing, a slippery beast we try to catch by the tail at any given moment that is constantly receding before us. And when predict it, we are saying more about the time in which we are living than anything that has yet to occur.
As William Gibson famously said: “…science fiction was always about the period in which it was written.” At every juncture in our history, what we perceive as being the future changes based on what’s going on at the time. And always, people love to bring up what has been predicted in the past and either fault or reward the authors for either “getting it right” or missing the mark.
 This would probably leave many people wondering what the point of it all is. Why not just wait and let the future tend to itself? Because it’s fun, that’s why! And as a science fiction writer, its an indispensable exercise. Hell, I’d argue its absolutely essential to society as a whole. As a friend of one once said, “science fiction is more of a vehicle than a genre.” The point is to make observations about society, life, history, and the rest.
This would probably leave many people wondering what the point of it all is. Why not just wait and let the future tend to itself? Because it’s fun, that’s why! And as a science fiction writer, its an indispensable exercise. Hell, I’d argue its absolutely essential to society as a whole. As a friend of one once said, “science fiction is more of a vehicle than a genre.” The point is to make observations about society, life, history, and the rest.
And sometimes, just sometimes, predictive writers get it right. And lately, I’ve been inspired by sources like Future Timeline to take a look at the kinds of predictions I began making when I started writing and revising them. Not only have times changed and forced me to revise my own predictions, but my research into what makes humanity tick and what we’re up to has come a long way.
So here’s my own prediction tree, looking at the next few centuries and whats likely to happen…
21st Century:
2013-2050:
- Ongoing recession in world economy, the United States ceases to be the greatest economic power
- China, India, Russia and Brazil boast highest rates of growth despite continued rates of poverty
- Oil prices spike due to disappearance of peak oil and costs of extracting tar sands
- Solar power, wind, tidal power growing in use, slowly replacing fossil fuel and coal
- First arcologies finished in China, Japan, Russia, India and the United States
- Humanity begins colonizing the Moon and mounts manned mission to Mars
- Settlements constructed using native soil and 3D printing/sintering technology
- NASA tows asteroid to near Earth and begins studies, leading to plans for asteroid mining
- Population grows to 9 billion, with over 6 living in major cities across the all five continents
- Climate Change leading to extensive drought and famine, as well as coastal storms, flooding and fires
- Cybernetics, nanotech and biotech leading to the elimination of disabilities
- 3D Construction and Computer-Assisted Design create inexpensive housing in developing world
- First exploratory mission to Europa mounted, discovers proof of basic life forms under the surface ice
- Rome ordains first openly homosexual priests, an extremely controversial move that splits the church
- First semi-sentient, Turing compatible AI’s are produced and put into service
- Thin, transparent, flexible medical patches leading to age of “digital medicine”
- Religious orders formed opposed to “augmentation”, “transhumanism” and androids
- First true quantum computers roll off the assembly line
- Creation of the worldwide quantum internet underway
- Quantum cryptography leads to increased security, spamming and hacking begins to drop
- Flexible, transparent smartphones, PDAs and tablets become the norm
- Fully immersive VR environments now available for recreational, commercial and educational use
- Carbon dioxide in the upper atmosphere passes 600 ppm, efforts to curb emissions are redoubled
- ISS is retired, replaced by multiple space stations servicing space shuttles and commercial firms
- World’s first orbital colony created with a population of 400 people
2050-2100:
- Global economy enters “Second Renaissance” as AI, nanomachinery, quantum computing, and clean energy lead to explosion in construction and development
- Commercial space travel become a major growth industry with regular trips to the Moon
- Implant technology removes the need for digital devices, technology now embeddable
- Medical implants leading to elimination of neurological disorders and injuries
- Synthetic food becoming the rage, 3D printers offering balanced nutrition with sustainability
- Canada, Russia, Argentina, and Brazil become leading exporters of foodstuffs, fresh water and natural gas
- Colonies on the Moon and Mars expand, new settlement missions plotted to Ganymede, Europa, Oberon and Titan
- Quantum internet expanding into space with quantum satellites, allowing off-world connectivity to worldwide web
- Self-sufficient buildings with water recycling, carbon capture and clean energy becomes the norm in all major cities
- Second and third generation “Martians” and “Loonies” are born, giving rise to colonial identity
- Asteroid Belt becomes greatest source of minerals, robotic foundries use sintering to create manufactured products
- Europe experiences record number of cold winters due to disruption of the Gulf Stream
- Missions mounted to extra-Solar systems using telexploration probes and space penetrators
- Average life expectancy now exceeds 100, healthy children expected to live to 120 years of age
- NASA, ESA, CNSA, RFSA, and ISRO begin mounting missions to exoplanets using robot ships and antimatter engines
- Private missions to exoplanets with cryogenically frozen volunteers and crowdfunded spaceships
- Severe refugee crises take place in South America, Southern Europe and South-East Asia
- Militarized borders and sea lanes trigger multiple humanitarian crises
- India and Pakistan go to war over Indus River as food shortages mount
- China clamps down on separatists in western provinces of Xinjian and Tibet to protect source of the Yangtze and Yellow River
- Biotechnology begins to grow, firms using bacteria to assemble structural materials
- Fully sentient AIs created and integrated into all aspects of life
- Traditionalist communities form, people seeking to disconnect from modern world and eschew enhancement
- Digital constructs become available, making neurological downloads available
- Nanotech research leading to machinery and materials assembled at the atomic level
- Traditional classrooms giving way to “virtual classrooms”, on-demand education by AI instructors
- Medical science, augmentation, pharmaceuticals and uploads lead to the first generation of human “Immortals”
- Orbital colonies gives way to Orbital Nexus, with hundreds of habitats being established
- Global population surpasses 12 billion despite widespread famine and displacement
- Solar, wind, tidal, and fusion power replace oil and coal as the dominant power source worldwide
- Census data shows half of world residents now have implants or augmentation of some kind
- Research into the Alcubierre Drive begins to bear experimental results
2100-2150:
- Climate Change and global population begin to level off
- First “Neural Collective” created, volunteers upload their thought patterns into matrix with others
- Transhumanism becomes established religion, espousing the concept of transcendence
- Widespread use of implants and augmentation leads to creation of new underclass called “organics”
- Solar power industry in the Middle East and North Africa leading to growth in local economies
- Biotech leads to growth of “glucose economy”, South American and Sub-Saharan economies leading in manufacture of biomaterials
- Population in Solar Colonies and Orbital Nexus reaches 100,000 and continues to grow
- Off-world industry continues to grow as Asteroid Belt and colonies provide the majority of Earth’s mineral needs
- Famine now widespread on all five continents, internalized food production in urban spaces continues
- UN gives way to UNE, United Nations of Earth, which has near-universal representation
- First test of Alcubierre FTL Drive successful, missions to neighboring systems planned
- Tensions begin to mount in Solar Colonies as pressure mounts to produce more agricultural goods
- Extinction rate of wild animals begins to drop off, efforts at ecological restoration continue
- First attempts to creating world religion are mounted, met with limited success
- Governments in most developed countries transitioning to “democratic anarchy”
- Political process and involvement becoming digitized as representation becomes obsolete
- “Super-sentience” emerges as people merge their neural patterns with each other or AIs
- Law reformed to recognize neural constructs and AIs as individuals, entitled to legal rights
- Biotech research merges with AI and nanotech to create first organic buildings with integrated intelligence
2150-2200:
- Majority of the world’s population live in arcologies and self-sufficient environments
- Census reveals over three quarters of world lives with implants or augmentation of some kind
- Population of Orbital Nexus, off-world settlements surpasses 1 million
- First traditionalist mission goes into space, seeking world insulated from rapid change and development
- Labor tensions and off-world riots lead to creation of Solar policing force with mandate to “keep the peace”
- First mission to extra=Solar planets arrive, robots begin surveying surface of Gliese 581 g, Gliese 667C c, HD 85512 b, HD 40307 g, Gliese 163 c, Tau Ceti e, Tau Ceti f
- Deep space missions planned and executed with Alcubierre Drive to distant worlds
- 1st Wave using relativistic engines and 2nd Wave using Alcubierre Drives meet up and begin colonizing exoplanets
- Neighboring star systems within 25 light years begin to be explored
- Terraforming begins on Mars, Venus and Europa using programmed strains of bacteria, nanobots, robots and satellites
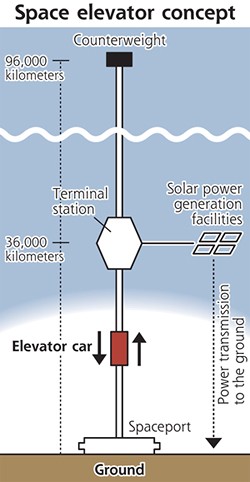
- Space Elevator and Slingatron built on the Moon, used to transport people to space and send goods to the surface
- Earth’s ecology begins to recover
- Natural species are reintroduced through cloning and habitat recovery
- Last reported famine on record, food production begins to move beyond urban farms
- Colonies within 50 light years are established on Gliese 163 c, Gliese 581 g, Gliese 667C c, HD 85512 b, HD 40307 g, Tau Ceti e, Tau Ceti f
- Off-world population reaches 5 million and continues to grow
- Tensions between Earth and Solar Colonies continue, lead to demands for interplanetary governing body
- Living, breathing cities become the norm on all settled worlds, entire communities build of integrated organic materials run by AIs and maintained by programmed DNA and machinery
23rd Century and Beyond:
Who the hell knows?
*Note: Predictions and dates are subject to revision based on ongoing developments and the author’s imagination. Not to be taken literally, and definitely open to input and suggestions.