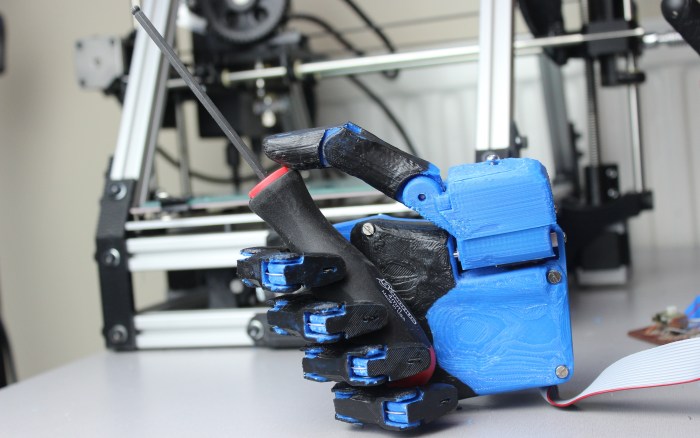
3-D Printing has been a boon for a number of industries, offering a cheaper method of production and sending those savings onto the consumer. One such industry is prosthetics, which is taking advantage of the new technology to cheaply generate all the components needed to create robotic replacement limbs. And with the proliferation of models, amputees and accident victims have a range of options that was previously unimaginable.
3-D Printing has been a boon for a number of industries, offering a cheaper method of production and sending those savings onto the consumer. One such industry is prosthetics, which is taking advantage of the new technology to cheaply generate all the components needed to create robotic replacement limbs. And with the proliferation of models, amputees and accident victims have a range of options that was previously unimaginable.
The latest comes to us from Bristol in the UK, where the robotics company known as The Open Hand Project has developed a robot limb that is cheaply produced and can be purchased for under £650 (or roughly $1000 US). At this price, their prosthetic device – known as the Dextrus robot hand = is significantly cheaper than existing robotics technology.
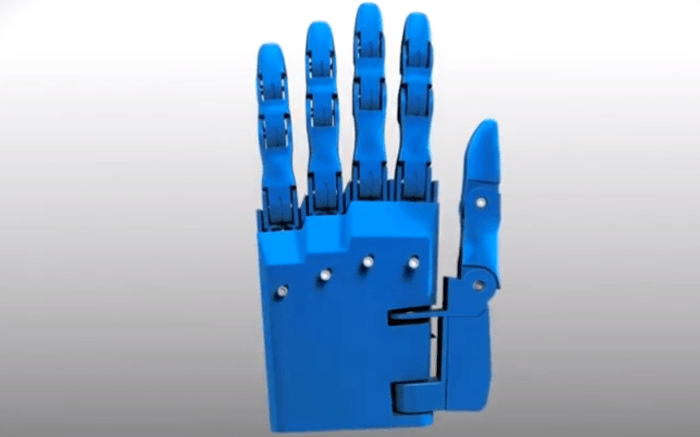 Inventor Joel Gibbard first came up with the idea for the Dextrus robotic hand while studying Robotics at the University of Plymouth in 2011. He developed a prototype for his final-year project before leaving to work for National Instruments. After two years in the workplace, he left his job in March 2013 to launch the Open Hand Project, an open-source venture that aims to make robotic prosthetic hands accessible for people in the developing world.
Inventor Joel Gibbard first came up with the idea for the Dextrus robotic hand while studying Robotics at the University of Plymouth in 2011. He developed a prototype for his final-year project before leaving to work for National Instruments. After two years in the workplace, he left his job in March 2013 to launch the Open Hand Project, an open-source venture that aims to make robotic prosthetic hands accessible for people in the developing world.
Gibbard’s hand relies entirely on off-the-shelf DC motors with a spool on the end that connects to a steel “tendon” that can be tightened and loosened when the user wants to move their fingers. The outer casing is composed of 3D-printed plastic parts that act like bones while a rubber coating acts as the skin. The user can control the fingers using electomyographical signals picked up from the muscle in their arm using stick-on electrodes.
 As Gibbard explained in an interview with Wired magazine:
As Gibbard explained in an interview with Wired magazine:
Each finger is individually actuated so you can grasp funny shaped objects. It’s not all that complicated. I’ve put a little tensioner in between each one so you have a bit of mechanical compliance. Even if an amputee has lost their hand, all of the muscles are still in the forearm and they can still flex them, so you can use that signal.
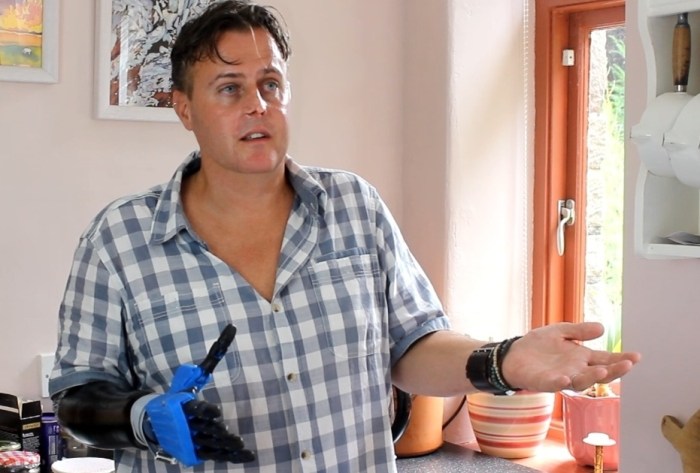
Already, the prosthesis was tested out by a chef named Liam Corbett, who lost his hand to meningitis two years ago and contacted Gibbard via Facebook when he heard about the Open Hand Project. According to Corbett, he was very impressed with the device and said that:
I think it’s certainly going to enable me to do the finer things in life which I certainly haven’t been able to do with a hook… I would be proud to wear this, it would make me feel more confident.
 Gibbard hopes to refine the design to cut down on the electrical noise it produces, and to develop specialized software to configure the electrodes to simplify the calibration process. Back in September, he opened up a crowdfunding campaign with Indiegogo to raise the necessary money. As of writing this article, he has surpassed his goal of £39,000 and raised a total of £41,065.
Gibbard hopes to refine the design to cut down on the electrical noise it produces, and to develop specialized software to configure the electrodes to simplify the calibration process. Back in September, he opened up a crowdfunding campaign with Indiegogo to raise the necessary money. As of writing this article, he has surpassed his goal of £39,000 and raised a total of £41,065.
However, there is still four days left before the campaign closes. So if you want to donate, thus enabling GIbbard and his colleagues to refine the design further, simply click here and follow the prompts. And be sure to check out the Indiegogo video to see how the hand works:
Sources: wired.co.uk, indiegogo.com