 Between artificial knees, total hip replacements, cataract surgery, hearing aids, dentures, and cochlear implants, we are a society that is fast becoming transhuman. Basically, this means we are dedicated to improving human health through substitution and augmentation of our body parts. Lately, bioprinting has begun offering solutions for replacement organs; but so far, a perfectly healthy heart, has remained elusive.
Between artificial knees, total hip replacements, cataract surgery, hearing aids, dentures, and cochlear implants, we are a society that is fast becoming transhuman. Basically, this means we are dedicated to improving human health through substitution and augmentation of our body parts. Lately, bioprinting has begun offering solutions for replacement organs; but so far, a perfectly healthy heart, has remained elusive.
Heart disease is the number one killer in North America, comparable only to strokes, and claiming nearly 600,000 lives every year in the US and 70,000 in Canada. But radical new medical technology may soon change that. There have been over 1,000 artificial heart transplant surgeries carried out in humans over the last 35 years, and over 11,000 more heart surgeries where valve pumps were installed have also been performed.
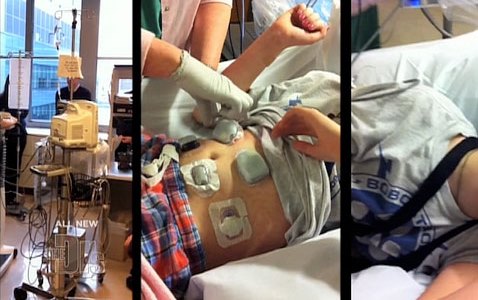
 And earlier this month, a major step was taken when the French company Carmat implanted a permanent artificial heart in a patient. This was the second time in history that this company performed a total artificial heart implant, the first time being back in December when they performed the implant surgery on a 76-year-old man in which no additional donor heart was sought. This was a major development for two reasons.
And earlier this month, a major step was taken when the French company Carmat implanted a permanent artificial heart in a patient. This was the second time in history that this company performed a total artificial heart implant, the first time being back in December when they performed the implant surgery on a 76-year-old man in which no additional donor heart was sought. This was a major development for two reasons.
For one, robotic organs are still limited to acting as a temporary bridge to buy patients precious time until a suitable biological heart becomes available. Second, transplanted biological hearts, while often successful, are very difficult to come by due to a shortage of suitable organs. Over 100,000 people around the world at any given time are waiting for a heart and there simply are not enough healthy hearts available for the thousands who need them.
 This shortage has prompted numerous medical companies to begin looking into the development of artificial hearts, where the creation of a successful and permanent robotic heart could generate billions of dollars and help revolutionize medicine and health care. Far from being a stopgap or temporary measure, these new hearts would be designed to last many years, maybe someday extending patients lives indefinitely.
This shortage has prompted numerous medical companies to begin looking into the development of artificial hearts, where the creation of a successful and permanent robotic heart could generate billions of dollars and help revolutionize medicine and health care. Far from being a stopgap or temporary measure, these new hearts would be designed to last many years, maybe someday extending patients lives indefinitely.
Carmat – led by co-founder and heart transplant specialist Dr. Alain Carpentier – spent 25 years developing the heart. The device weighs three times that of an average human heart, is made of soft “biomaterials,” and operates off a five-year lithium battery. The key difference between Carmat’s heart and past efforts is that Carmat’s is self-regulating, and actively seeks to mimic the real human heart, via an array of sophisticated sensors.
 Unfortunately, the patient who received the first Carmat heart died prematurely only a few months after its installation. Early indications showed that there was a short circuit in the device, but Carmat is still investigating the details of the death. On September 5th, however, another patient in France received the Carmat heart, and according to French Minister Marisol Touraine the “intervention confirms that heart transplant procedures are entering a new era.”
Unfortunately, the patient who received the first Carmat heart died prematurely only a few months after its installation. Early indications showed that there was a short circuit in the device, but Carmat is still investigating the details of the death. On September 5th, however, another patient in France received the Carmat heart, and according to French Minister Marisol Touraine the “intervention confirms that heart transplant procedures are entering a new era.”
More than just pumping blood, future artificial hearts are expected to bring numerous other advantages with them. Futurists and developers predict they will have computer chips and wi-fi capacity built into them, and people could be able to control their hearts with smart phones, tuning down its pumping capacity when they want to sleep, or tuning it up when they want to run marathons.
 The benefits are certainly apparent in this. With people able to tailor their own heart rates, they could control their stress reaction (thus eliminating the need for Xanax and beta blockers) and increase the rate of blood flow to ensure maximum physical performance. Future artificial hearts may also replace the need for some doctor visits and physicals, since it will be able to monitor health and vitals and relay that information to a database or device.
The benefits are certainly apparent in this. With people able to tailor their own heart rates, they could control their stress reaction (thus eliminating the need for Xanax and beta blockers) and increase the rate of blood flow to ensure maximum physical performance. Future artificial hearts may also replace the need for some doctor visits and physicals, since it will be able to monitor health and vitals and relay that information to a database or device.
In fact, much of the wearable medical tech that is in vogue right now will likely become obsolete once the artificial heart arrives in its perfected form. Naturally, health experts would find this problematic, since our hearts respond to our surroundings for a reason, and such stimuli could very well have unintended consequences. People tampering with their own heart rate could certainly do so irresponsibly, and end up causing damage other parts of their body.
 One major downside of artificial hearts is their exposure to being hacked thanks to their Wi-Fi capability. If organized criminals, an authoritarian government, or malignant hackers were dedicated enough, they could cause targeted heart failure. Viruses could also be sent into the heart’s software, or the password to the app controlling your heart could be stolen and misused.
One major downside of artificial hearts is their exposure to being hacked thanks to their Wi-Fi capability. If organized criminals, an authoritarian government, or malignant hackers were dedicated enough, they could cause targeted heart failure. Viruses could also be sent into the heart’s software, or the password to the app controlling your heart could be stolen and misused.
Naturally, there are also some critics who worry that, beyond the efficacy of the device itself, an artificial heart is too large a step towards becoming a cyborg. This is certainly true when it comes to all artificial replacements, such as limbs and biomedical implants, technology which is already available. Whenever a new device or technique is revealed, the specter of “cyborgs” is raised with uncomfortable implications.
 However, the benefit of an artificial heart is that it will be hidden inside the body, and it will soon be better than the real thing. And given that it could mean the difference between life and death, there are likely to be millions of people who will want one and are even willing to electively line up for one once they become available. The biggest dilemma with the heart will probably be affordability.
However, the benefit of an artificial heart is that it will be hidden inside the body, and it will soon be better than the real thing. And given that it could mean the difference between life and death, there are likely to be millions of people who will want one and are even willing to electively line up for one once they become available. The biggest dilemma with the heart will probably be affordability.
Currently, the Carmat heart costs about $200,000. However, this is to be expected when a new technology is still in its early development phase. In a few years time, when the technology becomes more widely available, it will likely drop in price to the point that they become much more affordable. And in time, it will be joined by other biotechnological replacements that, while artificial, are an undeniably improvement on the real thing.
The era of the Transhumanism looms!
Source: motherboard.vice.com, carmatsa.com, cdc.gov, heartandstroke.com






 At the time of the initial announcement in January, Google said its prototypes were able to take one glucose reading per second and that they was investigating ways for the device to act as an early warning system for the wearer should glucose levels become abnormal. All that was needed was a partner with the infrastructure and experience in the medical industry to see the prototypes put into production.
At the time of the initial announcement in January, Google said its prototypes were able to take one glucose reading per second and that they was investigating ways for the device to act as an early warning system for the wearer should glucose levels become abnormal. All that was needed was a partner with the infrastructure and experience in the medical industry to see the prototypes put into production.




 Android Wear takes much of the functionality of Google Now – an intelligent personal assistant – and uses the smartwatch as a home for receiving notifications and context-based information. For the sake of travel, Android Wear will push relevant flight, weather and other information directly to the watch, where the user can tap and swipe their way through it and use embedded prompts and voice control to take further actions, like dictating a note with reminders to pack rain gear.
Android Wear takes much of the functionality of Google Now – an intelligent personal assistant – and uses the smartwatch as a home for receiving notifications and context-based information. For the sake of travel, Android Wear will push relevant flight, weather and other information directly to the watch, where the user can tap and swipe their way through it and use embedded prompts and voice control to take further actions, like dictating a note with reminders to pack rain gear. Google officials also claimed at I/O that the same interface being Android Wear will be behind their new Android Auto and TV, two other integrated services that allow users to interface with their car and television via a mobile device. So don’t be surprised if you see someone unlocking or starting their car by talking into their watch in the near future. The first Android Wear watches – the Samsung Gear Live and the LG G Watch – are available to pre-order and the round-face Motorola Moto 360 is expected to come out later this summer.
Google officials also claimed at I/O that the same interface being Android Wear will be behind their new Android Auto and TV, two other integrated services that allow users to interface with their car and television via a mobile device. So don’t be surprised if you see someone unlocking or starting their car by talking into their watch in the near future. The first Android Wear watches – the Samsung Gear Live and the LG G Watch – are available to pre-order and the round-face Motorola Moto 360 is expected to come out later this summer. When it comes to the future, it is clear that the concept of the “Internet of Things” holds sway. This idea – which states that all objects will someday be identifiable thanks to a virtual representations on the internet – is at the center of a great deal of innovation that drives our modern economy. Be it wearables, wireless, augmented reality, voice or image recognition, that which helps us combine the real with the virtual are on the grow.
When it comes to the future, it is clear that the concept of the “Internet of Things” holds sway. This idea – which states that all objects will someday be identifiable thanks to a virtual representations on the internet – is at the center of a great deal of innovation that drives our modern economy. Be it wearables, wireless, augmented reality, voice or image recognition, that which helps us combine the real with the virtual are on the grow. As Ambarish Mitra, the head of Blippar stated, AR is already gaining traction among consumers thanks to some of the world’s biggest industrial players recognizing the shift to visually mediated lifestyles. Examples include IKEA’s interactive catalog, Heinz’s AR recipe booklet or Amazon’s recent integration of the Flow AR technology into its primary shopping app. As this trend continues, we will need a Wikipedia-like database for 3-D objects that will be available to us anytime, anywhere.
As Ambarish Mitra, the head of Blippar stated, AR is already gaining traction among consumers thanks to some of the world’s biggest industrial players recognizing the shift to visually mediated lifestyles. Examples include IKEA’s interactive catalog, Heinz’s AR recipe booklet or Amazon’s recent integration of the Flow AR technology into its primary shopping app. As this trend continues, we will need a Wikipedia-like database for 3-D objects that will be available to us anytime, anywhere.
 For better or for worse, wearable designs of consumer electronics have come to reflect a new understanding in the past few years. Basically, they have come to be extensions of our senses, much as Marshall McCluhan wrote in his 1964 book Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man. Google Glass is representative of this revolutionary change, a step in the direction of users interacting with the environment around them through technology.
For better or for worse, wearable designs of consumer electronics have come to reflect a new understanding in the past few years. Basically, they have come to be extensions of our senses, much as Marshall McCluhan wrote in his 1964 book Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man. Google Glass is representative of this revolutionary change, a step in the direction of users interacting with the environment around them through technology. Augmented reality has already proven itself to be a multi-million dollar industry – with 60 million users and around half a billion dollars in global revenues in 2013 alone. It’s expected to exceed $1 billion annually by 2015, and combined with a Google-Glass type device, this AR could eventually allow individuals to build vast libraries of data that will be the foundation for finding any 3-D object in the physical world.
Augmented reality has already proven itself to be a multi-million dollar industry – with 60 million users and around half a billion dollars in global revenues in 2013 alone. It’s expected to exceed $1 billion annually by 2015, and combined with a Google-Glass type device, this AR could eventually allow individuals to build vast libraries of data that will be the foundation for finding any 3-D object in the physical world.








 For some time now, classroom cameras have been used to see what teachers do in the course of their lessons, and evaluate their overall effectiveness as educators. But thanks to a recent advances in facial recognition software, a system has been devised that will assess teacher effectiveness by turning the cameras around and aiming at them at the class.
For some time now, classroom cameras have been used to see what teachers do in the course of their lessons, and evaluate their overall effectiveness as educators. But thanks to a recent advances in facial recognition software, a system has been devised that will assess teacher effectiveness by turning the cameras around and aiming at them at the class.
 After a lesson, a teacher could boot up EngageSense and see, with a glance at the dashboard, when students were paying rapt attention, and at what points they became confused or distracted. Beyond that, the concept is still being refined as SensorStar Labs looks both for funding and for schools to give EngageSense a real-world trial.
After a lesson, a teacher could boot up EngageSense and see, with a glance at the dashboard, when students were paying rapt attention, and at what points they became confused or distracted. Beyond that, the concept is still being refined as SensorStar Labs looks both for funding and for schools to give EngageSense a real-world trial. At the present time, the biggest obstacle would definitely be privacy concerns. While the software is designed for engaging student interest right now, it would not be difficult at all to imagine the same technology applied to police interrogations, security footage, or public surveillance.
At the present time, the biggest obstacle would definitely be privacy concerns. While the software is designed for engaging student interest right now, it would not be difficult at all to imagine the same technology applied to police interrogations, security footage, or public surveillance.















