 The skyline of the future… Chances are, it’s something we’ve all wondered about at one time or another. Given the current rate of urban expansion, combined with population growth and environmental concerns, it’s essentially a given that cities of the future will look quite different from cities today. And when it comes time to break new ground and convert old centers, contracts will be given to those designs that can meet all of these challenges.
The skyline of the future… Chances are, it’s something we’ve all wondered about at one time or another. Given the current rate of urban expansion, combined with population growth and environmental concerns, it’s essentially a given that cities of the future will look quite different from cities today. And when it comes time to break new ground and convert old centers, contracts will be given to those designs that can meet all of these challenges.
That’s the idea behind eVolo Magazine’s Skyscraper Competition, an annual event that for the past nine years has awarded architects and planners who create the problem-solving skyscrapers of the future. This year, over 600 entries were submitted from around the world, and top marks were given for those that addressed the problems or urban sprawl, pollution, sustainable living, and incorporated the latest in design technology.
These included the latest in renewable energy, carbon-capture technology, additive manufacturing (aka. 3D printing), and of course, the time honored concept of Paolo Soleri’s Arcology – a school of thought that merges architecture with ecology for smarter and more sustainable living. Here are just a few of the entries that received top marks in this year’s competition, which include the top three and numerous honorable mentions:
Winners:
Vernacular Versatility:
 The winner of this year’s Skyscraper Competition, this entry was created of Korean-American designer Yong Ju Lee. who used the concepts of the “Hanok” and “Gagu” as his inspiration. In traditional Korean architecture, the Hanok refers to a type of house with an exposed wooden structure and tiled roof. Gagu refers to a special wooden structural element that is located directly beneath the main roof where the column meets the beam and girder and fastens them without the need for nails or additional parts.
The winner of this year’s Skyscraper Competition, this entry was created of Korean-American designer Yong Ju Lee. who used the concepts of the “Hanok” and “Gagu” as his inspiration. In traditional Korean architecture, the Hanok refers to a type of house with an exposed wooden structure and tiled roof. Gagu refers to a special wooden structural element that is located directly beneath the main roof where the column meets the beam and girder and fastens them without the need for nails or additional parts.
Traditionally, this structural system has only ever been employed in the creation of single-story residences. However, modern modeling software allowed Lee to adapt this traditional system to complex high-rise structural planning to meet contemporary purposes and programs. Vernacular Versatility can open a new chapter of possibilities to bring this old construction and design tradition to the present day with efficiency and beauty.
Designed to be located within one of Korea’s busiest districts, Vernacular Versatility seeks to use a traditional design concept to combat the growing problem of urban sprawl, as well as associated health risks such as atopy and asthma, as well as addressing the destructive impacts urbanization has been having on traditional Korean culture and the environment.
Car and Shell Skyscraper: Also known as “Marinetti’s Monster” and created by Mark Talbot, Daniel Markiewicz, this concept for a “city in the sky” took home 2nd place at this year’s competition. As a solution for what to do about Detroit’s aging infrastructure, the project proposes a vertical suburban neighborhood equipped with recreational and commercial areas where three main grids (streets, pedestrian pathways, and structure) are intertwined to create a box-shaped wireframe.
Also known as “Marinetti’s Monster” and created by Mark Talbot, Daniel Markiewicz, this concept for a “city in the sky” took home 2nd place at this year’s competition. As a solution for what to do about Detroit’s aging infrastructure, the project proposes a vertical suburban neighborhood equipped with recreational and commercial areas where three main grids (streets, pedestrian pathways, and structure) are intertwined to create a box-shaped wireframe.
Inspired by all the attempts to “save Detroit”, which is focused largely on preserving its dwindling suburban areas, Talbot and Markiewicz instead thought of building a new neighborhood within a single enormous skyscraper located in the core. Here, dozens of single-family homes are stacked into a vertical grid, new roads cross through the building, and traditional and contemporary living all plug into a framework to create a rich urban environment.
Propagate Skyscraper:
 This year’s third place went to Canadian designers YuHao Liu and Rui Wu for their concept of a building that would turn air pollution into construction materials and use it to gradually create the building. Relying on an alternative carbon-capture technique that employs philic resins and material processes to transform carbon dioxide into solid construction material, their building employs additional material that uses carbon dioxide as a means to self-propagate.
This year’s third place went to Canadian designers YuHao Liu and Rui Wu for their concept of a building that would turn air pollution into construction materials and use it to gradually create the building. Relying on an alternative carbon-capture technique that employs philic resins and material processes to transform carbon dioxide into solid construction material, their building employs additional material that uses carbon dioxide as a means to self-propagate.
The building uses a simple vertical grid scaffold as a framework and takes all the ingredients it needs for material propagation from the surrounding environment. Individual living spaces are built within this gridwork, which creates open square spaces between lattices that can then be filled by tenements. Its pattern of growth is defined by environmental factors such as wind, weather, and the saturation of carbon dioxide within the immediate atmosphere.
Thus each building is a direct reflection of its environment, growing and adapting according to local conditions and cleaning as the air as it does so. Unlike conventional skyscrapers, which rely on steel frame and concrete casting, the proposed skyscraper suggests a more environmental conscious construction method, an alternative mode of occupation and ownership, and possibly a distinct organization of social relationships.
Honorable Mentions:
Climatology Tower:
 Designed by Yuan-Sung Hsiao, Yuko Ochiai, Jia-Wei Liu, Hung-Lin Hsieh and Japan and Taiwan, the Climatology Tower is a proposed skyscraper designed as a research center that evaluates urban meteorology and corrects the environment through mechanical engineering. This involves analyzing microclimates within cities as a result of the use of industrial materials, the accumulation of buildings, and the scarceness of open spaces. In order to maintain a healthy environment for the city, two main strategies are employed.
Designed by Yuan-Sung Hsiao, Yuko Ochiai, Jia-Wei Liu, Hung-Lin Hsieh and Japan and Taiwan, the Climatology Tower is a proposed skyscraper designed as a research center that evaluates urban meteorology and corrects the environment through mechanical engineering. This involves analyzing microclimates within cities as a result of the use of industrial materials, the accumulation of buildings, and the scarceness of open spaces. In order to maintain a healthy environment for the city, two main strategies are employed.
The first is Environmental Control Engineering, which consists of a system of evaluation and operational programs. Evaluation programs inspect city climates through a variety of factors such as insolation, radiation, and thermal coverage. Collected data is compared with humidity levels and then mechanical systems respond to reduce or increase the levels to optimal environmental conditions. The second is Information Expression, a system that is becoming increasingly common in East Asia.
Basically, in addition to automatically adjusting to optimal environmental conditions, data is transferred from a control center to different departments in this city. This can alert entire communities of present and upcoming environmental hazards and conditions, much as residents in major cities are currently given “smog alerts”. Climatic information is also displayed publicly, though digital networks, notifying the public on maintaining certain conditions, to preserve both energy and health.
Here-After: Designed by Tsang Aron Wai Chun of Hong Kong, the Here-After project is a proposal to reuse the Ruashi copper mine located in Lubumbashi, Congo. The mine is predicted to stop production in 2020, at which time it would be abandoned, leaving as an enormous urban void surrounded by a rapidly expanding city. The Here-After projects seeks to make use of the left over space, waste soil, and sulfuric acid from the mine drainage and former copper production.
Designed by Tsang Aron Wai Chun of Hong Kong, the Here-After project is a proposal to reuse the Ruashi copper mine located in Lubumbashi, Congo. The mine is predicted to stop production in 2020, at which time it would be abandoned, leaving as an enormous urban void surrounded by a rapidly expanding city. The Here-After projects seeks to make use of the left over space, waste soil, and sulfuric acid from the mine drainage and former copper production.
A machine will reuse the waste soil to neutralize the sulfuric acid, which in turn will be used to erode the land to be used as raw buildings blocks for the project. As the machine operates, starting from the South end, the remaining structures from the neutralization process would be reconfigured as a university campus. Throughout the building process the contour, the campus, and the public spaces would continuously change their relationships and form.
Hyper Filter Skyscraper:
 Designed by Umarov Alexey of Russia, the Hyper Filter Skyscraper recognizes the threat of environmental pollution and seeks to merge carbon capture technology with the building’s design. Under today’s levels of pollution, harmful substances spread over hundreds of kilometers and a whole region and even a country could represent a single pollution source. Hence the plan to place a air-scrubbing building at the heart of the problem – an urban core.
Designed by Umarov Alexey of Russia, the Hyper Filter Skyscraper recognizes the threat of environmental pollution and seeks to merge carbon capture technology with the building’s design. Under today’s levels of pollution, harmful substances spread over hundreds of kilometers and a whole region and even a country could represent a single pollution source. Hence the plan to place a air-scrubbing building at the heart of the problem – an urban core.
Consistent with CC technology and the principle of photosynthesis, the Hyper Filter Skyscraper is designed to inhale carbon dioxide and other harmful gases and exhale concentrated oxygen. The skin of the project is made out of long pipe filters that ensure the cleaning process. While clean air is released to the atmosphere, all the harmful substances are stored for use in the chemical industry for later use. These can include chemicals products, biofuels, and even manufactured goods.
Hyper-speed Vertical Train Hub:
 All around the world, nations from the USA, UK, Japan and China are again consolidating futuristic proposals for an advanced public transport network, to maximize the economic growth of their cities. The Hyper Speed Vertical Train Hub is an extension of this, aiming to resolve the inevitable challenges that cities will face by 2075, and offering a deliverable and sustainable solution for the future of the transport generation.
All around the world, nations from the USA, UK, Japan and China are again consolidating futuristic proposals for an advanced public transport network, to maximize the economic growth of their cities. The Hyper Speed Vertical Train Hub is an extension of this, aiming to resolve the inevitable challenges that cities will face by 2075, and offering a deliverable and sustainable solution for the future of the transport generation.
As the world’s population dramatically increases, the demand for goods, natural resources, foods, fuel and land would have increased significantly by 2075. By then, the world’s population will reach an estimated 10 or 11 million, and the majority of them (6 or 7 billion) will gravitate towards living in mega-cities. This will increase pressure and competition for adjacent suburban land, therefore forcing cities to explore more innovative forms of public transport.
 Consistent with a key principle of arcology, this proposal seeks to take advantage of vertical space in order to use available land more efficiently. By flipping the traditional form and function of the current train design into a vertical, cylindrical mass, the Vertical Train Hub seeks to eliminate the current impact that traditional stations have on land use, therefore returning the remaining site mass back to the densely packed urban Mega City.
Consistent with a key principle of arcology, this proposal seeks to take advantage of vertical space in order to use available land more efficiently. By flipping the traditional form and function of the current train design into a vertical, cylindrical mass, the Vertical Train Hub seeks to eliminate the current impact that traditional stations have on land use, therefore returning the remaining site mass back to the densely packed urban Mega City.
This remaining land will surround the base of the tower forming a large urban park, leading towards to the base of the Hyper-Speed Vertical Hub. The trains will create a dynamic and kinetic facade, one that will be continuously evolving and responsive to the workings of the vertical hub. Passengers will travel into the main lobby, allowing travelers to ascend through the atrium and through the platforms and onto the carriages. The high-speed trains will maximize time efficiency, able to traverse 482 km (300 miles) in just thirty minutes.
As the train travels and transitions from its horizontal formation, and ascends up the facade vertically, the carriages will pivot similar to that on a ‘Ferris wheel’, allowing the passengers within the carriage to remain in an upright position and facing towards the cityscape. The carriages will be supported by a magnetic structure located at either side, eliminating the need for rails beneath, and allowing the carriages and its passengers to connect to the tower.
Launchspire:
 Designed by Henry Smith, Adam Woodward, Paul Attkins of theUnited Kingdom, the Launchspire is an arcological design that also seeks to eliminate much of the CO2 emissions associated with air travel. This year, commercial air travel is celebrating its centenary; and looking ahead to 2050, aviation is predicted to fly 16 billion passengers and 400 million tones of cargo. This radical re-interpretation of the skyscraper would eliminate the hydrocarbon dependency of aircraft during takeoff through the use of an electromagnetic vertical accelerator.
Designed by Henry Smith, Adam Woodward, Paul Attkins of theUnited Kingdom, the Launchspire is an arcological design that also seeks to eliminate much of the CO2 emissions associated with air travel. This year, commercial air travel is celebrating its centenary; and looking ahead to 2050, aviation is predicted to fly 16 billion passengers and 400 million tones of cargo. This radical re-interpretation of the skyscraper would eliminate the hydrocarbon dependency of aircraft during takeoff through the use of an electromagnetic vertical accelerator.
On short flights, as much as 25% of the total fuel consumed is used during takeoff. The most fuel-efficient route length for airlines is 4,300 kilometers, but roughly half the flights taking place in the developed world cover less than 500 kilometers. An electromagnetic vertical accelerator, utilizing the technological principles developed at CERN’s LHC and maglev train propulsion, would provide a method for commercial aircraft to be accelerated to cruising speed using renewable electrical energy sources from ground-based infrastructure.
 This new design methodology envisions a ‘spiral tube’ structure that would reinvigorate the ‘core and floor plate’ model of high-rise buildings. Schools, hospitals, commercial, and residential properties would be interspersed throughout the tower with approximately one third of all Plots to be public green spaces, nature reserves and farm land. Due to the scale of the building, different climates would be experienced, with various wildlife and crop species, whilst also being natural devices for internal climate control.
This new design methodology envisions a ‘spiral tube’ structure that would reinvigorate the ‘core and floor plate’ model of high-rise buildings. Schools, hospitals, commercial, and residential properties would be interspersed throughout the tower with approximately one third of all Plots to be public green spaces, nature reserves and farm land. Due to the scale of the building, different climates would be experienced, with various wildlife and crop species, whilst also being natural devices for internal climate control.
The concept is essentially a helical version of the classic urban grid environment. This has the benefits of extreme high density, elevated living, mass transportation to different levels, pedestrian and cycle travel locally to enable healthy living. Community interaction and a unique and varied sense of place is achieved to each area of the tower. As the building ages specific areas develop to support an organic and culturally rich network of settlements within the matrix of the structure.
The towers can be built close to renewable energy infrastructures; hydropower in the mountains, tidal and offshore wind nearer the coast. The city is the building, the surrounding environment will remain natural thus the urban realm becomes a vertical entity within the wilderness. The building is effectively a confluence of road, rail, air and space transportation, and takes advantage of vertical spacing to reduce the impact on the local environment.
New Tower of Babel:
 Designed by Petko Stoevski of Germany, this perhaps unfortunately-named building seeks to invert the relationship between structures and their surrounding environment. Essentially, it is a steel construction built over a desert surface with multiple levels planned depending on the landscape’s topology. The top two panels are made of glass, and the air contained in between is warmed up by the sunlight. The structure is slightly tilted upwards, which leads the air to the middle of the tower into an inner cylindrical.
Designed by Petko Stoevski of Germany, this perhaps unfortunately-named building seeks to invert the relationship between structures and their surrounding environment. Essentially, it is a steel construction built over a desert surface with multiple levels planned depending on the landscape’s topology. The top two panels are made of glass, and the air contained in between is warmed up by the sunlight. The structure is slightly tilted upwards, which leads the air to the middle of the tower into an inner cylindrical.
The updraft power channels the warm air into the chimney tower, propelling the wind turbines located in the base and converting the kinetic energy into electrical power. Under the glass panels, photovoltaic panels are placed to generate electricity while reflecting the sunrays, thereby offering more warming. Moreover, the photovoltaic panels cast a shadow, cooling down the land’s surface and creating a microclimate that allows the creation of residential and recreational areas as well as the development of agriculture.
The Tower of Babel establishes a new landscape, which makes use of the natural forces of an upwind power plant and therefore stretches from the horizontal to the vertical. The building is characterized by many different spaces and leaves their use open to improvisation. Therefore, life develops in different places with different intensity. The project reinforces the principles of sustainability, which allow long term economic, social, and ecological development.
PleXus Tower:
 Designed by Chris Thackrey, Steven Ma, Bao An Nguyen Phuoc, Christos Koukis, Matus Nedecky, Stefan Turcovsky of the United States, the PleXus Tower is proposed development for the West Hong Kong Harbor. It was conceived as a segmented, but highly connected network of major transportation functions, as well as housing conventional program, that would merge the concepts of interconnectedness, renewable energy, and ecology into the same fabric.
Designed by Chris Thackrey, Steven Ma, Bao An Nguyen Phuoc, Christos Koukis, Matus Nedecky, Stefan Turcovsky of the United States, the PleXus Tower is proposed development for the West Hong Kong Harbor. It was conceived as a segmented, but highly connected network of major transportation functions, as well as housing conventional program, that would merge the concepts of interconnectedness, renewable energy, and ecology into the same fabric.
The design starts out as a series of distributed pods reaching out to connect with the city’s transportation, accepting traffic in the form of boats, ferries, and other water vehicles. Bridged together by connected pipelines over the water, these pods work in harmony with the existing Macau Ferry Terminal. As people move inward from these pods, they travel through a series of different structures, beginning with a horizontal parking structure that also connects to the highway network to efficiently receive car traffic.
 Farther up, business and shopping space is available, all accessible by car to the highest level of the tower. The upper reaches of the towers are set aside for residential space, providing a living area that incorporates spectacular views of the dynamic city skyline. A heliport on top that can receive air traffic from above, and power is supplied by the south-facing side of the building that comes equipped with numerous solar panels.
Farther up, business and shopping space is available, all accessible by car to the highest level of the tower. The upper reaches of the towers are set aside for residential space, providing a living area that incorporates spectacular views of the dynamic city skyline. A heliport on top that can receive air traffic from above, and power is supplied by the south-facing side of the building that comes equipped with numerous solar panels.
The skin is also breathable, with numerous openings designed to overlap each other, undulating throughout, allowing carbon dioxide to easily filter out from the designated parking areas on the lower levels. Each parking level will also utilize foliage to further filter carbon dioxide from the air helping to reduce pollution in Hong Kong. At night, lights will glow from the panels, reminding people of the connections these segments share as well as blending in with Hong Kong’s unique night skyline.
Project Blue:
 Designed by Yang Siqi, Zhan Beidi, Zhao Renbo, Zhang Tianshuo of China, Project Blue is designed with China’s explosive growth in mind. On the one hand, the country’s “economic miracle” has left the world in awe. But on the other, the country is paying a big price for being the “factory of the world”, in the form of getting polluted at an alarming speed. Chinese cities are now characterized by an unhealthy hazy weather as the result of large amounts of suspended particles in the air.
Designed by Yang Siqi, Zhan Beidi, Zhao Renbo, Zhang Tianshuo of China, Project Blue is designed with China’s explosive growth in mind. On the one hand, the country’s “economic miracle” has left the world in awe. But on the other, the country is paying a big price for being the “factory of the world”, in the form of getting polluted at an alarming speed. Chinese cities are now characterized by an unhealthy hazy weather as the result of large amounts of suspended particles in the air.
The purpose of Project Blue is to transform suspended particles into green energy by creating an enormous upside down cooling tower with a multi-tubular cyclic desulfurization system that produces nitrogen and sulfur. When both elements are combined with the atmospheres surplus of carbon monoxide, the result is “water coal” that would later be transformed into methane through a low-pressure reaction called low pressure efficient mathanation.
This methane could then be converted into biofuel that would then be shipped to the surface, providing a clean alternative for China’s fast-growing supply of gasoline cars. Consistent with many modern designs that utilize carbon capture technology, Project Blue would therefore be combating the problem of emissions and air pollution at both ends.
Rainforest Guardian:
 While most of the concepts were designed for cities, a few were made for more remote locations. The Rainforest Guardian, from Chinese architects Jie Huang, Jin Wei, Qiaowan Tang, Yiwei Yu, and Zhe Hao, was one such example. Designed to sit on the edge of the Amazon, capturing and storing rainwater in the rainy season to help fight fires in the dry season, the building also has labs located at the top for scientists studying and monitoring the local environment.
While most of the concepts were designed for cities, a few were made for more remote locations. The Rainforest Guardian, from Chinese architects Jie Huang, Jin Wei, Qiaowan Tang, Yiwei Yu, and Zhe Hao, was one such example. Designed to sit on the edge of the Amazon, capturing and storing rainwater in the rainy season to help fight fires in the dry season, the building also has labs located at the top for scientists studying and monitoring the local environment.
The lotus-shaped water tower is captures rainwater directly and then filters and stores it in its spare reservoirs. Using capillarity combined with active energy, the aerial roots with a distinct sponge-structure can absorb and store the excess water without disturbing the Amazon’s ecosystem. In the case of fire, firefighters fly to the scene and extinguish the fire with the collected water. In addition, the laboratories can act as exhibition spaces for tourists to create environmental awareness.
Sand Babel:
 Produced by designers Qiu Song, Kang Pengfei, Bai Ying, Ren Nuoya, and Guo Shen of China, the Sand Babel uses an idea similar to that being proposed by NASA and the ESA to build settlements on the Moon. Basically, their plan is to use sintering and additive manufacturing to turn desert sand into a series of ecological skyscrapers.These structures would serve as scientific research and testing facilities, tourist attractions for the desert, and would be divided into two parts.
Produced by designers Qiu Song, Kang Pengfei, Bai Ying, Ren Nuoya, and Guo Shen of China, the Sand Babel uses an idea similar to that being proposed by NASA and the ESA to build settlements on the Moon. Basically, their plan is to use sintering and additive manufacturing to turn desert sand into a series of ecological skyscrapers.These structures would serve as scientific research and testing facilities, tourist attractions for the desert, and would be divided into two parts.
The first part, located above ground, consists of several independent structures for a desert community while the second part, located partially underground, would connect several different buildings together and create a multi-functional tube network system. The main portion of each building is constructed with sand, sintered through a solar-powered 3D printer to create walls of solid ceramic.
The top structures utilizes a spiral skeleton shape, inspired by desert phenomena like Tornadoes and mushroom rocks. These are tall, straight and have high tensile strength, and are thus able to withstand high winds. The net structure of the lower sections are similar to tree roots, effectively anchoring each building into the ground. The dual funnel model provides cooling through cross-ventilation, as well as ensuring that water can be collected through condensation.
Seawer:
 Designed by Sung Jin Cho of South Korea, the Seawer was inspired by another major environmental issue – the problem of waste. Every year, millions of tons of trash enter the ocean, and between 60 and 80 percent of it is from land-based sources. Due to ocean currents, this waste collects in particular areas of the world, such as the one currently located in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Consisting of tiny particles of plastics, this area is commonly referred as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP), or just “Garbage Island”.
Designed by Sung Jin Cho of South Korea, the Seawer was inspired by another major environmental issue – the problem of waste. Every year, millions of tons of trash enter the ocean, and between 60 and 80 percent of it is from land-based sources. Due to ocean currents, this waste collects in particular areas of the world, such as the one currently located in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Consisting of tiny particles of plastics, this area is commonly referred as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP), or just “Garbage Island”.
The GPGP is twice the size of Texas and contains six times more plastic than plankton biomass. And since plastic is not biodegrade, it poses a threat to thousands of marine animals. Seawer proposes to install a huge drainage hole 550 meters in diameter and 300 meters in depth in the middle of the GPGP that would engulf all kinds of floating trash filled with seawater. Seawer consists of five layers of baleen filters, which separate particles and fluids and collected the particles together.
 These collected plastics are then taken to a recycling plant atop of the structure while seawater is filtered and stored in a large sedimentation tank at the bottom to be further cleaned and released into the ocean. Much like skyscrapers that are energy-independent and turn air pollution into useable fuels, the Seawer concept is all about making a future city that can offer solutions, and placing it at the heart of the problem.
These collected plastics are then taken to a recycling plant atop of the structure while seawater is filtered and stored in a large sedimentation tank at the bottom to be further cleaned and released into the ocean. Much like skyscrapers that are energy-independent and turn air pollution into useable fuels, the Seawer concept is all about making a future city that can offer solutions, and placing it at the heart of the problem.
Skyvillage:
 Designed by Ziwei Song of the United States, the Skyvillage concept was inspired by Los Angeles’s freeway system, which he claims segregates the city’s fabric and restricts urban activities to single locations. As a result, Song envisioned a vertical city that would encourage urban integration by providing a bridge over freeway interruptions and connect the four quadrants around the 101 and 110 freeways. This single architectural organism would also boost cultural exchanges, urban activities, and social interaction.
Designed by Ziwei Song of the United States, the Skyvillage concept was inspired by Los Angeles’s freeway system, which he claims segregates the city’s fabric and restricts urban activities to single locations. As a result, Song envisioned a vertical city that would encourage urban integration by providing a bridge over freeway interruptions and connect the four quadrants around the 101 and 110 freeways. This single architectural organism would also boost cultural exchanges, urban activities, and social interaction.
The interchange 101 and 110 breaks Los Angeles east urban fabric into four disconnected quadrants: Downtown, Chinatown, Echo Park, and Temple Beaudry. The four quadrants have distinct cultural and social differences, lacking a coherent urban tissue. Moreover, the leftover space around the freeways reaches over 27 acres. Skyvillage aims to reclaim this vague terrain and provide green filtering towers to clean the freeways and also articulate various programs to revitalize the disconnected urban fabric.
Urban Alloy Structure:
 Last, but certainly not least, there is the design concept that was put forth this year by Matt Bowles and Chad Kellogg of the United States. Known as Urban Alloy, the concept was inspired by cities like New York and other dynamic cities of the 21st century – which they refer to as “anthropomorphic alloys”. In short, these cities act as engines for innovation and social cohesion which, combined with their continually evolving demographics, will forge the dynamic societies of the future.
Last, but certainly not least, there is the design concept that was put forth this year by Matt Bowles and Chad Kellogg of the United States. Known as Urban Alloy, the concept was inspired by cities like New York and other dynamic cities of the 21st century – which they refer to as “anthropomorphic alloys”. In short, these cities act as engines for innovation and social cohesion which, combined with their continually evolving demographics, will forge the dynamic societies of the future.
Once again, the concept calls for smart growth – developments that promote innovation and renewal without disrupting current land use. Hence their proposal for a residential typology that surrounds the intersection of transportation hubs – such as elevated train lines and freeway interchanges – with a set of highly linked living environments that capture the air rights above these systems. The design and skin of the structure also reflects a blend of space types and a desire to optimized shading and day lighting.
 Composed of a series of different alloys and composites, the system is deployed on a grid that follows the geometric pattern of the surface. This grid is designed for integration with adjoining pieces of the structure, and to optimize shading and lighting so the building doesn’t cast a huge shadow over adjacent areas (which is a common problem for skyscrapers). The resulting architecture is a steel diagrid system that can efficiently be constructed with each unique member cut by an automated system (i.e. 3D metal printing)
Composed of a series of different alloys and composites, the system is deployed on a grid that follows the geometric pattern of the surface. This grid is designed for integration with adjoining pieces of the structure, and to optimize shading and lighting so the building doesn’t cast a huge shadow over adjacent areas (which is a common problem for skyscrapers). The resulting architecture is a steel diagrid system that can efficiently be constructed with each unique member cut by an automated system (i.e. 3D metal printing)
The relatively light weight of each structural unit also means that it can be constructed with greater ease, cutting down on construction costs and the carbon foot involved. The wall systems are also built with a high content of recycled materials, making it a comparatively eco-friendly structure compared to most modern skyscrapers.
Summary:
An impressive collection, isn’t it? And this is not even the complete list of winners and runner-ups, just those that I felt I could squeeze in to this here humble post. Alas, it gives a pretty good idea what the great minds of the world are coming up with when they consider the needs of urban residents and cityscapes in the coming years and decades. In addition to providing housing, energy, transportation and basic services in ways that are sustainable, top marks go to those who can turn problems into solutions.
When Paolo Soleri first conceived of his Arcology concept, he was looking for a way to provide room for more people with less space, and in a way that did not further tax the environment. However, since the 1970’s, this challenge has been updated thanks to the advance of Climate Change. At this juncture, simply not adding to the problem is no longer sufficient. Future living solutions must also find ways to reduce and roll back the damage.
Hence concepts that now call for carbon capture, garbage processing, and pollution control in addition to the smart use of space, urban agriculture, and renewable energy. It is one of the paradoxes of the modern age that cities are both the cause, and solution to, the problems of modern living. While they may bring millions of people together in one place, producing tons of waste and pollution, they also bring together ideas for change and innovation that lead to better living.
In the end, ideas that expand upon this paradox – turning cities into pollution and garbage-eating factories – will not only determine the size and shape of future cities, they may very well ensure the survival of the natural environment and the human race itself. Much like all life on this planet, we remain permanently connected to space and place and are dependent on it for our livelihood and our very lives. The only way to keep living in to learn to live with it.
For more info on eVolo’s 2014 Skyscraper Competition, or to just check out some interesting design and architecture news, click on this link to go to their homepage.
Sources: fascoexist.com, (2), evolvo.us
 Hey all! Just wanted to do a late trip update and let everybody know I’m still kicking, and to share some of the many experiences that were had so far on this trip. It’s been almost two weeks now since the family and I departed from Vancouver Island and landed on the Continent, and try as I might, I’ve been unable to resist my internet fix! So as long as I was surfing, checking messages and doing a little messaging myself, I figured I could at least post an update or two.
Hey all! Just wanted to do a late trip update and let everybody know I’m still kicking, and to share some of the many experiences that were had so far on this trip. It’s been almost two weeks now since the family and I departed from Vancouver Island and landed on the Continent, and try as I might, I’ve been unable to resist my internet fix! So as long as I was surfing, checking messages and doing a little messaging myself, I figured I could at least post an update or two. But before that, we were in the Flanders region of Belgium and the Normandy region of France. We began with Ypres, a small city in Belgium that was the site of three major battles during the Great War. This began in 1914 when the Allies retook the town from the Germans after their great sweep into northern France failed. The second took place five months later when the Germans, hoping to break the stalemate in Belgium, used chlorine gas for the first time. It was during this gas attack that the Canadian 1st Division distinguished itself by holding its ground and repelling the attack, despite the fact that they had no gas masks. The third and final battle took place east of the city and is also known as the Battle of Passchendaele, one of the bloodiest of the war.
But before that, we were in the Flanders region of Belgium and the Normandy region of France. We began with Ypres, a small city in Belgium that was the site of three major battles during the Great War. This began in 1914 when the Allies retook the town from the Germans after their great sweep into northern France failed. The second took place five months later when the Germans, hoping to break the stalemate in Belgium, used chlorine gas for the first time. It was during this gas attack that the Canadian 1st Division distinguished itself by holding its ground and repelling the attack, despite the fact that they had no gas masks. The third and final battle took place east of the city and is also known as the Battle of Passchendaele, one of the bloodiest of the war. We were also sure to visit the cemeteries, battlefields and memorials at Beaumont-Hamel, Concrete Farm, Langemarck, St. Julien, and Tyne Cot. This last cemetery, which is the largest World War I cemetery ever, has a small museum where the names of every soldier who died in the Battle of Arras is named. The recording plays on a loop, and takes FIFTEEN YEARS to finish!
We were also sure to visit the cemeteries, battlefields and memorials at Beaumont-Hamel, Concrete Farm, Langemarck, St. Julien, and Tyne Cot. This last cemetery, which is the largest World War I cemetery ever, has a small museum where the names of every soldier who died in the Battle of Arras is named. The recording plays on a loop, and takes FIFTEEN YEARS to finish! After that, we visited the Vimy Memorial in France, one of the greatest to come out of the war. This site, and the many preserved trenches, tunnels and craters that mark the landscape are preserved and attended to by Canadian students who hope to keep the memory of this historical battle alive. Not only was it a major victory for the allies – the first decisive offensive of the war – it also defined Canada as a nation. While being guided through the trenches and tunnel, my father and I once again paused to pick up some keepsakes. This time around, it was a piece of chalk and flint (which the ridge is made of) and a small bit of ceramic, possibly from an old teacup.
After that, we visited the Vimy Memorial in France, one of the greatest to come out of the war. This site, and the many preserved trenches, tunnels and craters that mark the landscape are preserved and attended to by Canadian students who hope to keep the memory of this historical battle alive. Not only was it a major victory for the allies – the first decisive offensive of the war – it also defined Canada as a nation. While being guided through the trenches and tunnel, my father and I once again paused to pick up some keepsakes. This time around, it was a piece of chalk and flint (which the ridge is made of) and a small bit of ceramic, possibly from an old teacup. This was perhaps the most interesting part of our journey since it involved retracing the path of an actual family member. His name was Wilmot Pettit, and on June 6th, 1944, he was shot down while towing a glider full of British Commandos into the Normandy countryside. The mayor of Grangues was extremely helpful, and drove us to where the crash took place, told of how the survivors had been captured and executed by the SS, offered to send us some photos of the downed plane, and told us where Wilmott had been buried. We then drove to the cemetery at Ranville to pay our respects, before heading on to Bayeux.
This was perhaps the most interesting part of our journey since it involved retracing the path of an actual family member. His name was Wilmot Pettit, and on June 6th, 1944, he was shot down while towing a glider full of British Commandos into the Normandy countryside. The mayor of Grangues was extremely helpful, and drove us to where the crash took place, told of how the survivors had been captured and executed by the SS, offered to send us some photos of the downed plane, and told us where Wilmott had been buried. We then drove to the cemetery at Ranville to pay our respects, before heading on to Bayeux.









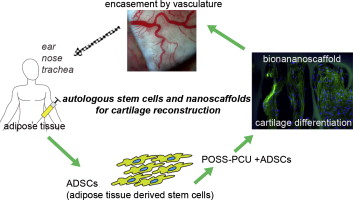
 There is also the potential to begin reconstructive treatment with stem cells derived from adipose tissue earlier than previously possible, as it takes time for the ribs to grow enough cartilage to undergo the procedure. As Dr. Patrizia Ferretti, a researcher working on the project, said in a recent interview:
There is also the potential to begin reconstructive treatment with stem cells derived from adipose tissue earlier than previously possible, as it takes time for the ribs to grow enough cartilage to undergo the procedure. As Dr. Patrizia Ferretti, a researcher working on the project, said in a recent interview:



 And unlike the current microgravity suits, the Z-series is designed for walking in extra-terrestrial environments where gravity is the norm (i.e. the Moon and Mars). Intrinsic to the new design is flexibility: it makes it much easier to walk, bend, and pick things up off the surface of a planet or moon. It also goes on quite differently. Whereas the old suit is pulled on like a pair of pants and a shirt, the new version has a handy door built into the back so someone can climb inside.
And unlike the current microgravity suits, the Z-series is designed for walking in extra-terrestrial environments where gravity is the norm (i.e. the Moon and Mars). Intrinsic to the new design is flexibility: it makes it much easier to walk, bend, and pick things up off the surface of a planet or moon. It also goes on quite differently. Whereas the old suit is pulled on like a pair of pants and a shirt, the new version has a handy door built into the back so someone can climb inside.










 Consistent with a key principle of arcology, this proposal seeks to take advantage of vertical space in order to use available land more efficiently. By flipping the traditional form and function of the current train design into a vertical, cylindrical mass, the Vertical Train Hub seeks to eliminate the current impact that traditional stations have on land use, therefore returning the remaining site mass back to the densely packed urban Mega City.
Consistent with a key principle of arcology, this proposal seeks to take advantage of vertical space in order to use available land more efficiently. By flipping the traditional form and function of the current train design into a vertical, cylindrical mass, the Vertical Train Hub seeks to eliminate the current impact that traditional stations have on land use, therefore returning the remaining site mass back to the densely packed urban Mega City.

















 The ability to tailor-make synthetic bones, which are exact duplicates to the original, offers exciting possibilities for reconstructive and replacement surgery. It also does away with some rather invasive and unsatisfactory procedures that involve putting shattered bones back together and joining them with pins, bars and screws. And considering that such procedures often require multiple operations, the combination of 3D scanning and 3D printed replacements is also far more cost effective.
The ability to tailor-make synthetic bones, which are exact duplicates to the original, offers exciting possibilities for reconstructive and replacement surgery. It also does away with some rather invasive and unsatisfactory procedures that involve putting shattered bones back together and joining them with pins, bars and screws. And considering that such procedures often require multiple operations, the combination of 3D scanning and 3D printed replacements is also far more cost effective.
 But the good news is, I don’t plan on stopping there. The whole point of initiating this promotion was to get people primed and ready to read the second book in the series – Papa Zulu – which was released a little over a month ago. Naturally, I needed for prospective readers to be caught up on everything in the first book before I could interest them in the second. And now that I’ve managed to get a few people in on that, I thought a second promotion might be in order.
But the good news is, I don’t plan on stopping there. The whole point of initiating this promotion was to get people primed and ready to read the second book in the series – Papa Zulu – which was released a little over a month ago. Naturally, I needed for prospective readers to be caught up on everything in the first book before I could interest them in the second. And now that I’ve managed to get a few people in on that, I thought a second promotion might be in order. You might think this is all about selling more books, but in truth, my full motives are have to do with getting people to read these books in sequence. As everyone is no doubt aware, you can’t start a series partway through anymore than you could start scaling a building somewhere in the middle. You got to get in on the ground floor and see where everything goes as you slowly make your way to the top.
You might think this is all about selling more books, but in truth, my full motives are have to do with getting people to read these books in sequence. As everyone is no doubt aware, you can’t start a series partway through anymore than you could start scaling a building somewhere in the middle. You got to get in on the ground floor and see where everything goes as you slowly make your way to the top.